RBI Repo Policy February 2026: Rate Held at 5.25% as MPC Signals Neutral Stance
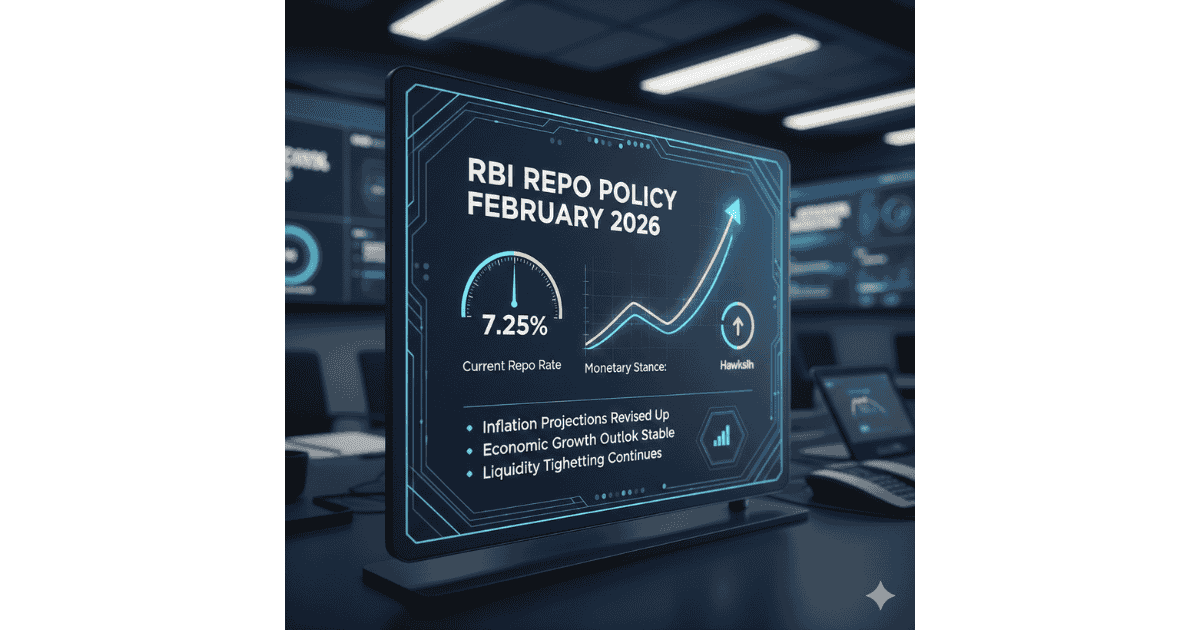
The RBI repo policy February 2026 kept the benchmark policy rate unchanged, with the Monetary Policy Committee maintaining a neutral stance as inflation remained contained and growth momentum stayed resilient. The decision signals a pause after the recent rate-cut cycle and reflects the central bank’s attempt to balance domestic growth with global uncertainties and commodity-price risks.
Live Data Box — RBI Policy February 2026
- Repo Rate: 5.25% (unchanged)
- Policy Stance: Neutral
- SDF Rate: 5.00%
- MSF / Bank Rate: 5.50%
- Inflation Outlook: Around 2.1% for FY26
Source: RBI Monetary Policy Committee February 2026 announcement
Table of Contents
- Policy Decision Overview
- Key Rates and Stance
- Inflation Outlook
- Growth Projections
- Liquidity and Transmission Strategy
- Rate Cycle Context
- Banking Sector Impact
- Bond Market Implications
- Equity Market Capital Flows
- Sector-Wise Impact Analysis
- Global Macro Context
- Institutional Capital-Flow Impact
- Policy Outlook and Rate Trajectory
- Key Takeaways
Policy Decision Overview
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee unanimously decided to keep the repo rate unchanged at 5.25% in its February 2026 policy meeting. The central bank also retained its neutral stance, signaling that future rate decisions will depend on evolving inflation and growth conditions.
The move was widely expected by markets, as inflation remained under control while growth indicators showed resilience.
Key Rates and Stance
Under the February policy decision:
- Repo rate remained at 5.25%
- Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate at 5.00%
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) and bank rate at 5.50%
- Policy stance retained as neutral
The neutral stance indicates that the central bank is neither committing to further easing nor tightening, leaving room for data-dependent adjustments.
Inflation Outlook
Inflation conditions played a key role in the policy decision.
- CPI inflation projected around 2.1% for FY26
- Inflation remained below the RBI’s 4% target for several months
However, the RBI highlighted potential risks:
- Commodity price volatility
- Global uncertainties
- Adverse weather conditions affecting food inflation
This balance between low current inflation and emerging risks contributed to the policy pause.
RBI Repo Policy February 2026: Growth Projections
The RBI maintained a constructive outlook on economic growth.
- GDP growth projected around 7.4%
- Domestic demand and infrastructure spending remain strong drivers
The central bank indicated that growth momentum appears durable, allowing it to pause rate cuts without jeopardizing economic expansion.
Liquidity and Transmission Strategy
Alongside the rate decision, the RBI emphasized proactive liquidity management.
The central bank stated it would conduct calibrated liquidity operations to:
- Ensure effective policy transmission
- Address imbalances from forex interventions
- Manage government cash flows
This indicates a shift from rate-cut focus to liquidity and transmission efficiency.
Rate Cycle Context
The February 2026 policy comes after a series of rate cuts during 2025.
- Repo rate reduced by 125 basis points since early 2025
- December 2025 policy included a 25 bps cut to 5.25%
The February decision therefore signals a potential end to the easing cycle.
Banking Sector Impact
A stable repo rate affects the banking system in multiple ways.
Lending rates
- No immediate change in loan EMIs expected
Deposit rates
- Fixed deposit rates likely to remain stable in the near term
For banks, a pause in the rate cycle typically:
- Stabilizes net interest margins
- Improves earnings visibility
- Reduces volatility in funding costs
RBI Repo Policy February 2026: Bond Market Implications
The bond market tends to respond quickly to policy signals.
After the policy:
- Bond yields rose slightly due to lack of additional liquidity measures
- Market reaction remained relatively stable overall
A pause in the rate-cut cycle usually results in:
- Stabilizing yields
- Reduced duration gains
- Shift toward carry strategies
Equity Market Capital Flows
The policy decision influences capital allocation across sectors.
Banking and financials
- Stable rates support margins
- Improved earnings visibility
Real estate
- Unchanged rates keep home loans affordable
- Positive demand outlook for housing
Consumption
- Stable EMIs support discretionary demand
Sector-Wise Impact Analysis
1) Banking and NBFCs
- Margin stability improves earnings predictability
- Credit growth remains supported by stable borrowing costs
2) Real Estate
- Stable home loan rates support housing demand
- Developer sentiment improves due to financing stability
3) Automobiles
- Consumer loan rates remain stable
- Supports demand for passenger vehicles
4) Infrastructure
- Long-term borrowing costs remain predictable
- Supports project financing cycles
RBI Repo Policy February 2026: Global Macro Context
The RBI’s decision also reflects external developments.
- Trade agreements with the US and EU improved economic outlook
- Global uncertainties and commodity price risks remain
Foreign portfolio flows also showed improvement:
- $1 billion equity inflows after earlier outflows
Institutional Capital-Flow Impact
1) Pause in Easing Cycle
After multiple rate cuts, the February decision signals a pause, which:
- Stabilizes bond yields
- Improves banking sector outlook
2) Financial Sector Support
Stable rates generally benefit:
- Banks
- NBFCs
- Insurance companies
3) Real Estate Demand Stability
Unchanged rates maintain affordability for borrowers, supporting:
- Housing demand
- Developer balance sheets
4) Selective Equity Rotation
Institutional flows may rotate toward:
- Financials
- Real estate
- Rate-sensitive sectors
RBI Repo Policy February 2026: Policy Outlook and Rate Trajectory
The neutral stance suggests the RBI is entering a wait-and-watch phase.
For rate cuts
- Sharp slowdown in growth
- Sustained low inflation
For rate hikes
- Commodity price shocks
- Food inflation spikes
- Currency volatility
Economists expect the central bank to remain on hold unless macro conditions change significantly.
Key Takeaways
- Repo rate held at 5.25%
- Policy stance remains neutral
- Inflation outlook remains benign
- Growth momentum considered durable
- Rate-cut cycle likely entering a pause phase